Windows 11 GPU Hardware Accelerated Scheduling: How does it work?
Windows 11 offers one of the significant advancements when it comes to gaming, and two important factors are dominating it. First is the Auto HDR Feature, and second is the Direct Storage, which allows GPUs to access the storage directly. There is another factor called GPU Hardware Accelerated Scheduling. It not only improves game performance but overall experience on Windows 11 when it comes to graphics and CPU-intensive apps.
In this post, we are looking at the last one, also called GPU Hardware Scheduling, and how it works in Windows 11.
What is Windows 11 GPU Hardware Accelerated Scheduling?
Before we talk about this feature, let’s connect the dots on how it all came together.
VRAM:
A video RAM or Video Random Access Memory is a type of RAM that is specifically designed to store image data for a computer display.
It ensures an even and smooth display of graphics, and Game designers or any GPU-intensive application uses this.
How did it work before this feature?
Now that we know about VRAM, let’s understand how things were handled earlier. Windows has a component Windows Display Driver Model that, along with GPU scheduling, submitted any graphics-related work to a global queue handled by the CPU. This process has its challenge as the work queued up, and it was too much for the system.
That is where the GPU Hardware Accelerated Scheduling comes into the picture, where Windows OS starts offloading high-frequency tasks to the GPU-based scheduler.
How does it help?
Scheduling GPU processes using hardware acceleration makes it possible to run applications more efficiently. The GPU now manages VRAM instead of Windows OS, which decreases latency & increases performance. How does this help? In simple words, the ability for GPU workload management to be improved by moving scheduling responsibilities into hardware from software could lead to enhanced GPU responsiveness and further innovations.
That said, the CPU still controls prioritization. It gives a final decision on which applications have priority.
How to enable GPU Hardware Scheduling?
You can enable it via Settings and the Registry Changes.
Via Settings
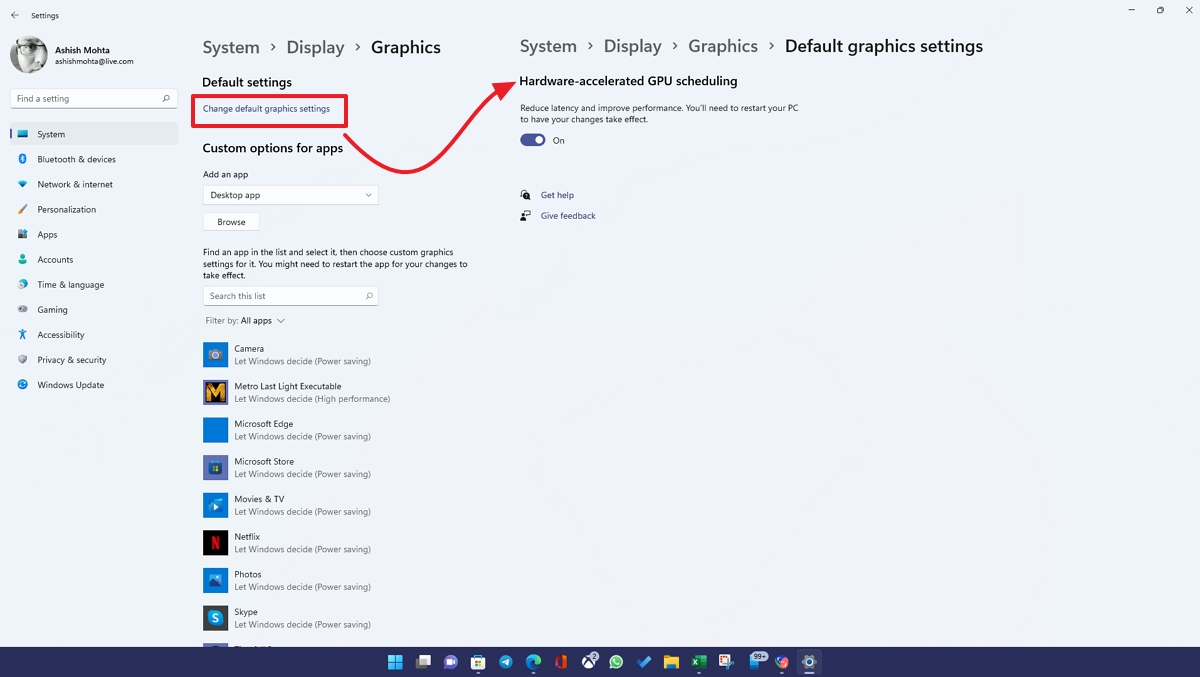
- Open Windows 11 Settings (Win + I)
- Navigate to System > Display > Graphics
- Click on the Change Default graphics settings link
- Toggle on the option under Hardware-accelerated GPU Scheduling.
- Restart PC to apply the changes.
This feature works with both NVIDIA and AMD Graphics drivers that use WDDM 2.7.
Via Registry
This method is useful when you need to enable it on a remote computer, or you plan to export a modified key and apply it to multiple computers.
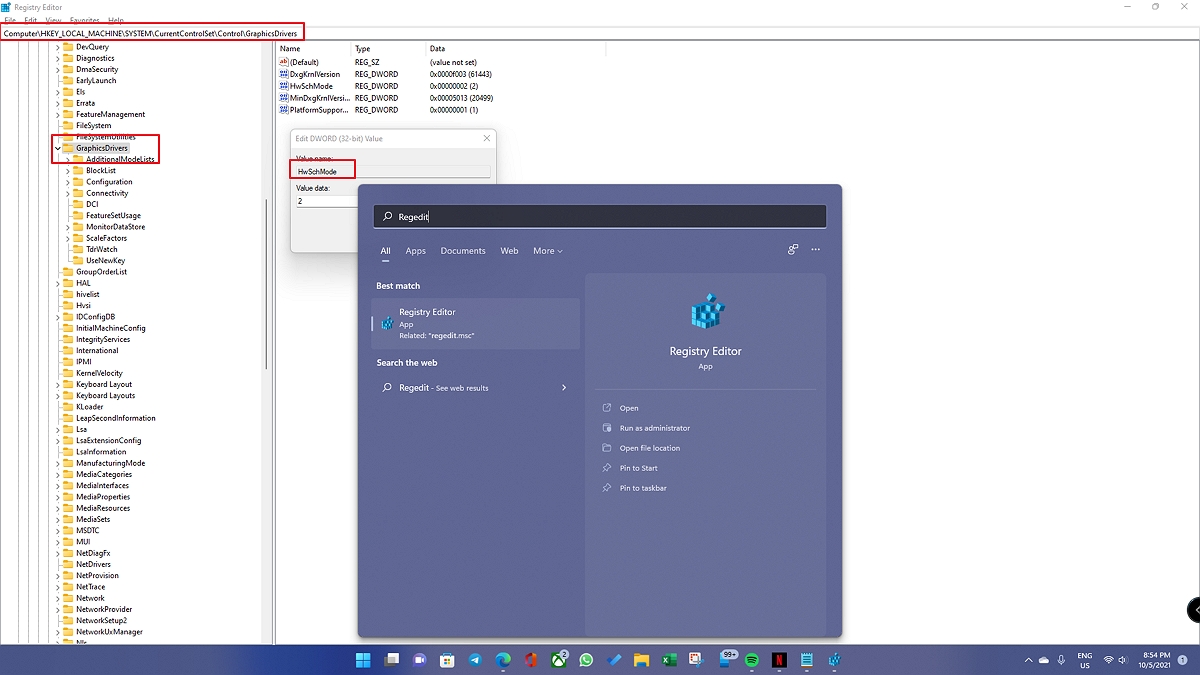
- Open Run prompt using Win + R
- Type Regedit, and press the Enter key
- Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control > GraphicsDrivers
- Double click on DWORD HwSchMode.
- Set the Base to Hexadecimal.
- Set Value data to 2.
- Click on the OK button to save the changes.
- Restart your PC.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Should You Enable GPU Hardware Scheduling?
Going by the CPU logic, this feature should be useful on mid-tier hardware where you rely more on CPU and don’t have a dedicated Graphics Card that should be able to take advantage of this feature.
Does it improve CPU-based gaming performance?
Theoretically yes. Those games which rely more on CPU than GPU should see improved frame rate as work has been offloaded to the GPU. While one may not know the result on high-end configuration, those with lower configuration should see this happening, especially if the CPU usage hits 100%.
Does Hardware-accelerated GPU Scheduling make a difference?
It does, especially in the case of intense gaming, streaming videos, and apps that primarily use the GPU. However, in day-to-day tasks, you may not feel a lot of it.