Guide to Disk management in Windows 11
Windows as an OS takes a lot more space than previous versions, but the amount of storage occupied by user files has also increased multifold. It is either the data or games or backups that take a lot of space. With time, you will need to manage them by moving files where space is more or adding storage space to increase existing partitions, merging them, or creating new ones.
All this needs the right set of tools. This post will look at the Disk Management in Windows 11 and software you can use to get this most easily by taking a few precautions.
Windows 11 Disk Management

Diskpart is a command-line tool in Windows 11 that can help you manage storage devices. Built using the same APIs is the Disk Management which delivers a UI that allows general users to manage disks. The command-line tool can be cumbersome, but those who are good at it will find it very useful.
When you launch the tool, it will display a list of connected storage devices and partitions of all the drives in one place.
Functions of Disk Management Tool
Volume or Partition operations:
- Create, Format, Delete, Shrink, Extend partitions
- Mark partition as active to change boot drive without changing boot order
- Change Drive Letter & Paths
- Add Mirror in case of Drive failure
Disk Operations:
- Spanned, Striped, Mirrored, Raid 5
- Convert to Dynamic Disk & MBR
- Take a disk offline
While the tool looks robust, it does have its drawbacks. There is no way you can preview what will happen when you take action. Also, there is no way to undo the changes, which means if you accidentally delete a partition or the disk, then there is no way to bring the data back.
How to use Disk Management Tool?
While you can perform any type of there are many types of operation that can be performed; in this example, we will show how you can create a new partition.
Step 1: Press the Start button on the keyboard and type Create and format hard disk partition. Once it appears in the list, click to open the Disk Management tool.
Step 2: Right-click on a volume that is black and marked unallocated. Select New Volume and follow the wizard to set a drive letter, file system, and label.
Step 3: Once the wizard completes the job, the partition will be ready to use.
Similarly, other operations can be performed, and while some will be as simple as this, operations, where you create RAID volume will be different. As we are dealing with live data, I recommend performing these operations on an external hard disk that doesn’t have any data inside it.
Third-Party Disk Management Tools for Windows 11
The biggest caveat using the built-in disk management tool of Windows is that even with straightforward options, it can be confusing. And with no preview, it becomes easy to make mistakes. That’s where the third-party tools come into the picture.
While there are many, these two third-party disk management tools are the best in this segment. Keeping in mind that they offer competitive features and don’t cost a dime to the user.
1] Paragon Partition Manager

If you want an open-source solution that is backed by a community, then Paragon Software offers one. The community edition Partition Manager is free for personal and home usage. On top of this, it carries an excellent user interface and everything you could expect from a disk management tool.
Features:
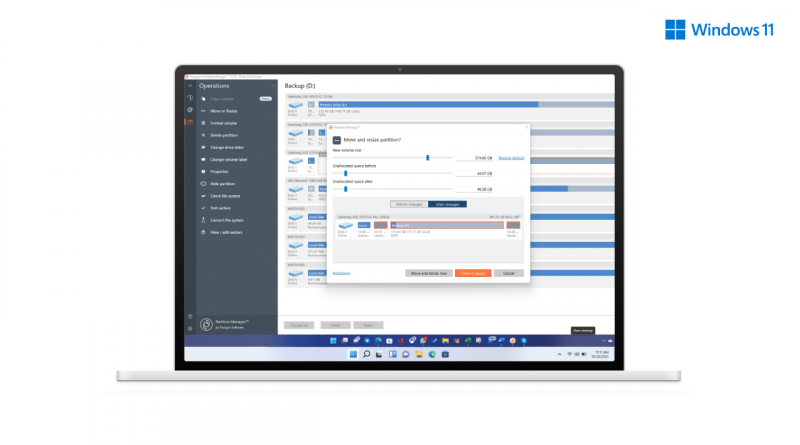
The best feature of using this tool is that it comes with an undo button that allows you to see a preview of any disk operation you perform.
Once you launch the software, it will list down all the partitions. Please select any of them, and it offers direct functions, including Move or Resizes, Delete, change volume label, check file system, test surface. You can also view or edit sectors, but that is best left for advanced users.
The operations are not executed immediately, but instead, you get the option to place it in the queue. Once you are through that this is what you wanted as the final state, execute the queue.
- Convert between MBR to GPT / HFS volumes to NTFS
- No formatting is required when converting between the formats.
- Recover deleted volumes using Undelete function
That said, the software also has few drawbacks. You cannot create a clone if you are migrating storage devices, i.e., moving from HDD to SSD or between SSDs. Also, there is no way to securely erase a hard disk if you give it to someone else.
2] Partition Expert Free Edition (Macrorit)

If you are looking for a portable disk manager software that supports Windows Storage Space, then Macrorit’s Partition Expert Free Edition has you covered. While it’s a free version, it limits only those parts used for commercial purposes such as migrating OS, creating WinPE bootable disk, etc.
Features
Once you launch the software, all operations are on the left side, while all partitions or volumes are listed on the right, sorted by drive. Select any of the drives, and you can choose operations on the left or right-click and get disk-specific options.
If you have a planned set of operations that needs to be executed one after the other, you can set them up and execute them in a row. All the functions that you plan are available under pending operations.
- Complete disk management solution
- Conversion to a logical volume
- Wipe Volume, Format, Surface Test
- Undo, Redo operations
Overall, it’s excellent software that offers a more intuitive and easy way to use the software.
Conclusion
Windows 11, like its predecessors, comes with in-house disk managing software, which works most of the time; it can be used from both the command line and through the UI. However, the software is raw; there is no way to fall back and revert, making it cumbersome. That’s where their third-party disk management software comes into play. Make sure to try all of them before making a final choice.